Deep Muscles of the Thorax Promote Movements for Breathing
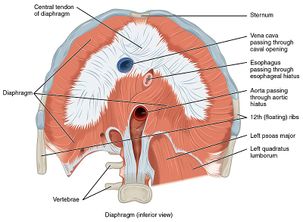
It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavity by its thin and dome shaped structure. The major muscle responsible for helping us breathe is the diaphragm.
Muscles Of Respiration Physiopedia
A respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration.
. The thoracic wall is essential to this process and is made up of the sternum 12 pairs of ribs 12 thoracic vertebrae and the muscles fascia and skin that connect to this bony cage. Glue lungs maintain contact with thoracic wall and diaphragm. Pulmonary ventilation more commonly referred to as breathing is the movement of air into and out of the lungs.
The diaphragm can be located below the lungs and consists of a sheet of skeletal muscle which displays a double-domed structure. Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps. Pleural fluid in pleural space.
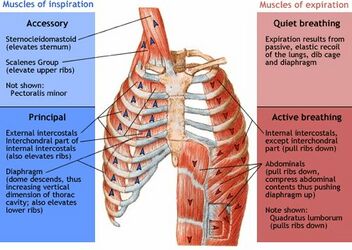
Muscles of the thorax for breathing and the pelvic floor the diaphragm We have 3 layers of muscles that prevent the organs from falling down. Contraction of external intercostals. In addition accessory muscles primarily the internal intercostals help to compress the rib cage which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity.
The diaphragm is important as it separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and therefore requires 3 openings that act as channels for. Inspiratory muscles peaceful breathing. Inhalation is the act of drawing air into the lungs and exhalation is the.
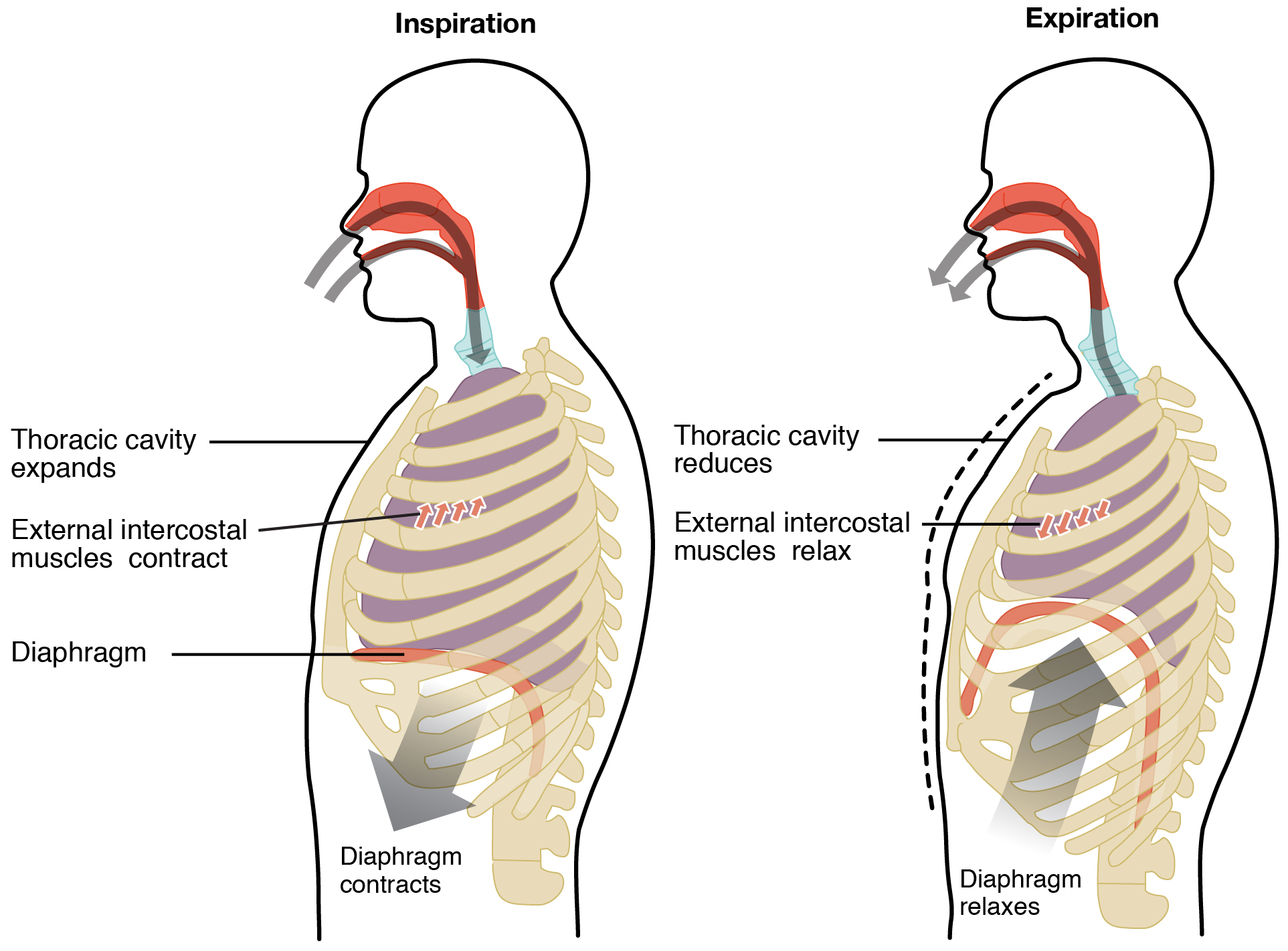
When it contracts and flattens the volume inside the pleural cavities increases which decreases the pressure within them. The vastus lateralis True TF Deep muscles of the thorax promote movements for breathing. Inspiration is the process that causes air to enter the lungs and expiration is the process that causes air to leave the lungs Figure 2233.
The fourth article in this five-part series on respiratory rate expands on the procedure to measure respiratory rate outlined in part 3 and provides a guide to the assessment of respiratory rhythm and chest movement. Spinalis the main extensor backward bending muscle of the thoracic spine located on either side of the vertebral column. Self-Stretching Stretches and self-mobilizations work on the muscles soft tissue neural tissue and the joints in the upper back.
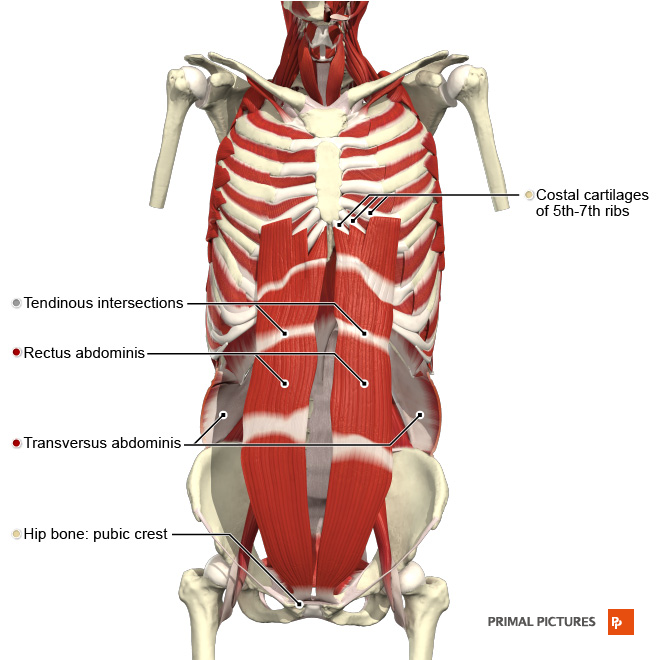
Wheatley I 2018 Respiratory rate 4. Sternocleidomastoid scalene muscles serratus anterior pectoralis major pectoralis minor trapezius latissimus dorsi erector spinae iliocostalis lumborum quadratus lumborum. The muscles of the thorax include both the diaphragm as well as the muscles of the thoracic cage.
Lie on your side with your knees bent. If volume of thoracic cavity increases causes lung volume to increase. These muscles act to change the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration.
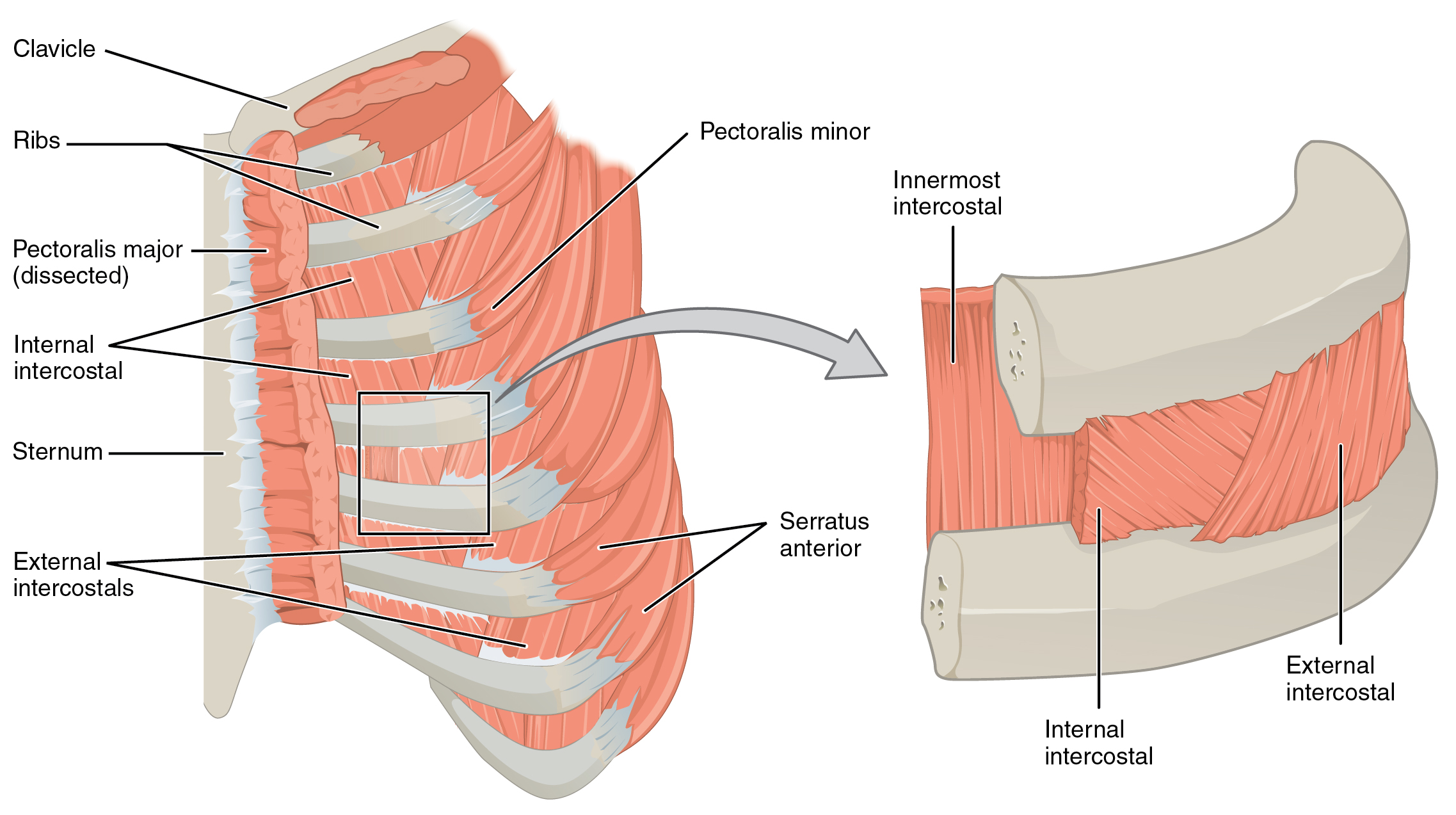
Most important muscle in respiration Seperates thorax from abdomen External Intercostals 11 Pairs that lie BETWEEN ribs. The frontal belly of the epicranius. Elevate rib cage Synergists to Diaphragm in ACTIVE inspiration.
1Thoracic Erector Spinae group ie Iliocostalis. List the 3 muscles of the thorax. Breathing rhythm and chest movement provide key information on a patients condition.
The opposite action causes exhalation. Inhalation at rest AND vigorous exercise. True TF The muscles of facial expression insert into skin or other muscles not bones.
Straighten your arms and use them to rotate your upper back. O-inferior border of rib above. There are some other muscles that do not comprise the thoracic wall but do attach to it.
I-superior border of rib below. The deep muscle of the thorax that promote the inspiratory phase of breathing is the external intercostal. False TF Although all skeletal muscles have different shapes the fascicle arrangement of each muscle is exactly the same.
Here are some physiotherapy exercises that can enhance your thoracic spine flexibility and help you breathe better. Public symphysis coccyx ischial tuberosities. Colloquially we call this the diaphragm.
With first ribs fixed by scalene muscles pull ribs toward one another to elevate rib cage. There are five muscles that make up the thoracic cage. Respiratory Volumes and Capacities Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory cycle.
In the thoracic region it is deep to the trapezius and rhomboids. In the lumbar region it is deep to the latissimus dorsi. It is a muscle that originates from the lower border of a rib.
As a result air will flow into the lungs. Ribs move forward and upward. The muscles of the thorax play a large role in breathing especially the dome-shaped diaphragm.
Diaphragm is the main inspiratory muscle during inspiration it contracts and moves in an inferior direction that increases the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity and produces lung expansion in turn the air is drawn in9 Intercostal musclesedit edit source. When the diaphragm contracts its central portion moves downwards and sides move upwards and cause inhalation. The erector spinae is most massive in the lumbar and thoracic regions.
Accesory inspiratory muscles used in respiratory distress. Note that the perineum is the diamond-shaped area defined by these four landmarks. The intercostals external internal and innermost subcostals and transversus thoracis.
External intercostals internal intercostals diaphragm.
Axial Muscles Of The Abdominal Wall And Thorax Anatomy And Physiology
Muscles Of Respiration Physiopedia
No comments for "Deep Muscles of the Thorax Promote Movements for Breathing"
Post a Comment